
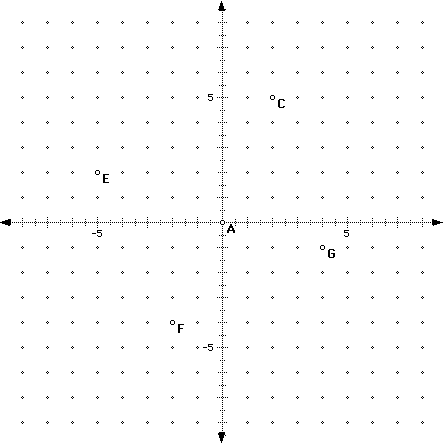
However, humans have long had some conception of negative numbers, due to phenomena such as measuring sea level or debt. Historically, negative numbers largely came about as a way of solving equations that otherwise wouldn't have solutions, such as x + 8 = 3. Notice that 0 is the only number whose opposite is itself. The integer numbers (or simply integers) extend whole numbers to their opposites. If we start counting from 0 instead, the set of numbers are instead called whole numbers. These are the counting numbers that start with 1, 2, and 3, and go on forever.
#Quadrant 1 2 3 4 graph serial
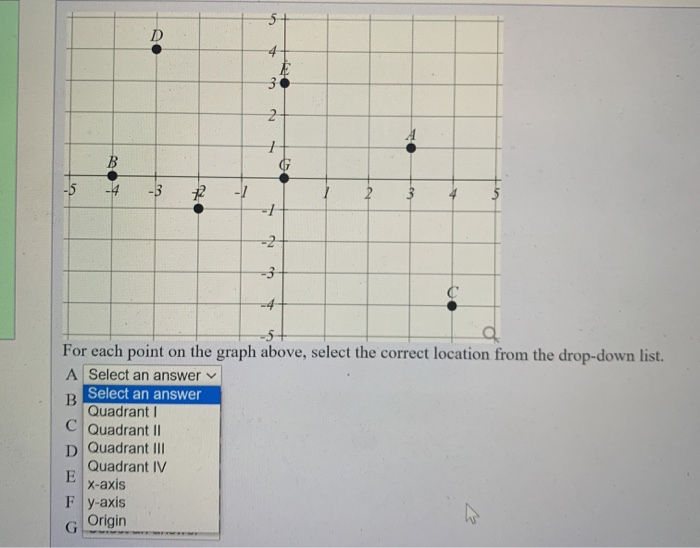
The most common numbers that we encounter-in everything from speed limits to serial numbers-are natural numbers. The numbers in an ordered pair are called coordinates. Note that the point (3,2) is not the same as point (2,3).

The second number tells how far up or down the point is located in the vertical direction.

The first number tells how far to the right or left the point is located in the horizontal direction. ( Common Core 6.NS.C.8, Florida BEST MA.6.GR.1.1)Ī location, or point, on a grid can be identified by an ordered pair such as (3,2), which names the coordinates of that point. Key Standard: Graph points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane.Once they are ready for positive and negative integers, often by Grade 6, you can extend graphing to all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. In the U.S., students in Grades 5 and up typically first learn to perform x- and y-axis graphing on a coordinate plane. A coordinate plane graph lives in the space between writing and drawing mathematics, as the graph can often be described both by written equations and visual shapes.
#Quadrant 1 2 3 4 graph how to
One way is to separate the subject into how to write math (oftentimes, algebra) and how to draw it (oftentimes, geometry). There are many ways to think fundamentally about the concept of mathematics. ICLE (International Center for Leadership in Education)Ĭustomer Service & Technical Support Portal Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12 That’s all you need to know.Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5 You figured out that the intercepts of the line this equation represents are (0,2) and (3,0). Once you have found the two intercepts, draw a line through them. You can use intercepts to graph linear equations. To find the x– and y-intercepts of a linear equation, you can substitute 0 for y and for x respectively.įor example, the linear equation 3y+2x=6 has an x intercept when y=0, so 3\left(0\right)+2x=6\\. Notice that the y-intercept always occurs where x=0, and the x-intercept always occurs where y=0. The y-intercept above is the point (0, 2). The x-intercept above is the point (−2,0). Every point on this line is a solution to the linear equation. The arrows at each end of the graph indicate that the line continues endlessly in both directions. Then you draw a line through the points to show all of the points that are on the line. However, it’s always a good idea to plot more than two points to avoid possible errors. Two points are enough to determine a line. One way is to create a table of values for x and y, and then plot these ordered pairs on the coordinate plane.
There are several ways to create a graph from a linear equation. A linear equation is an equation with two variables whose ordered pairs graph as a straight line. There are multiple ways to represent a linear relationship-a table, a linear graph, and there is also a linear equation. In this case, the relationship is that the y-value is twice the x-value. You can think of a line, then, as a collection of an infinite number of individual points that share the same mathematical relationship. Look at how all of the points blend together to create a line. You have likely used a coordinate plane before. The coordinate plane consists of a horizontal axis and a vertical axis, number lines that intersect at right angles. This system allows us to describe algebraic relationships in a visual sense, and also helps us create and interpret algebraic concepts. The coordinate plane can be used to plot points and graph lines. In his honor, the system is sometimes called the Cartesian coordinate system. The coordinate plane was developed centuries ago and refined by the French mathematician René Descartes. (1.3.1) – Plotting points on a coordinate plane (1.3.5) – Graphing other equations using a table or ordered pairs.(1.3.4) – Recognizing and using intercepts.(1.3.3) – Determine whether an ordered pair is a solution of an equation.(1.3.2) – Create a table of ordered pairs from a two-variable linear equation and graph.(1.3.1) – Plotting points on a coordinate plane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
